Unlocking the potential of RNN and CNN models for accurate rehabilitation exercise classification on multi-datasets
Jan 1, 2025·,,,·
1 min read
Moamen Zaher
Amr S Ghoneim
Laila Abdelhamid
Ayman Atia
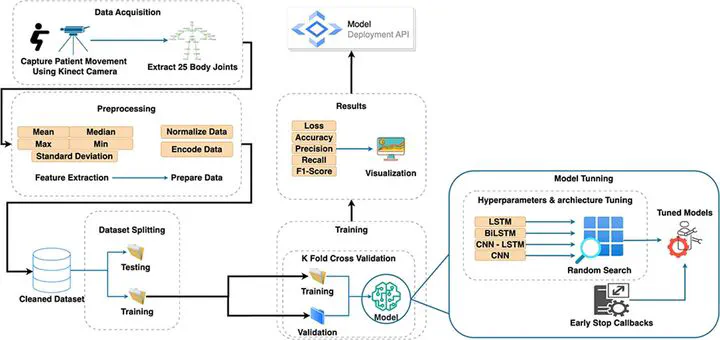 Image credit:
Image credit:Abstract
Physical rehabilitation is crucial in healthcare, facilitating recovery from injuries or illnesses and improving overall health. However, a notable global challenge stems from the shortage of professional physiotherapists, particularly acute in some developing countries, where the ratio can be as low as one physiotherapist per 100,000 individuals. To address these challenges and elevate patient care, the field of physical rehabilitation is progressively integrating Computer Vision and Human Activity Recognition (HAR) techniques. Numerous research efforts aim to explore methodologies that assist in rehabilitation exercises and evaluate patient movements, which is crucial as incorrect exercises can potentially worsen conditions. This study investigates applying various deep-learning models for classifying exercises using the benchmark KIMORE and UI-PRMD datasets. Employing Bi-LSTM, LSTM, CNN, and CNN-LSTM, alongside a Random Search for architectural design and Hyper-parameter tuning, our investigation reveals the (CNN) model as the top performer. After applying cross-validation, the technique achieves remarkable mean testing accuracy rates of 93.08% on the KIMORE dataset and 99.7% on the UI-PRMD dataset. This marks a slight improvement of 0.75% and 0.1%, respectively, compared to previous techniques. In addition, expanding beyond exercise classification, this study explores the KIMORE dataset’s utility for disease identification, where the (CNN) model consistently demonstrates an outstanding accuracy of 89.87%, indicating its promising role in both exercises and disease identification within the context of physical rehabilitation.
Type
Publication
Citations
This is my top-cited paper with +30 citations.